Mitochondria: The Powerhouses of Hormone Production
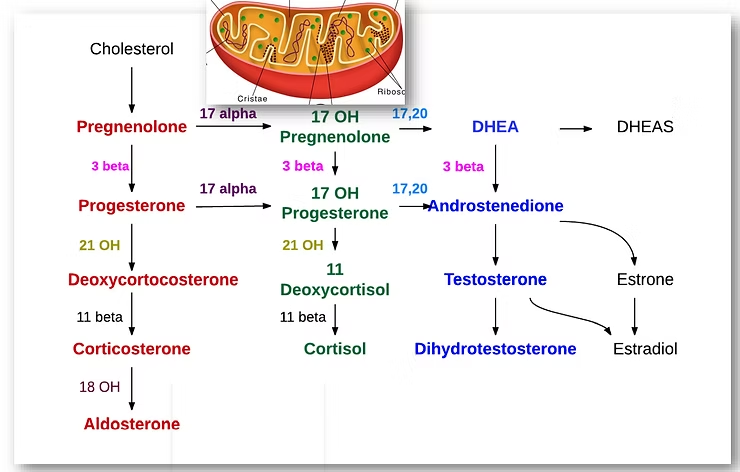
Mitochondria, the powerhouses of the human body, play a vital role in processing oxygen and converting nutrients from food into energy. Found in almost every cell, mitochondria are responsible for generating 90% of the energy required for the body to function optimally. However, the relationship between mitochondria and hormones goes beyond energy production. Hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, DHEA, as well as adrenal hormones like norepinephrine, epinephrine, and cortisol, are all closely linked to mitochondria. When mitochondria become sick or function poorly, hormonal imbalances can occur, leading to various mitochondrial diseases and disorders. This article aims to explore the effects of insufficient mitochondria on hormone production in the body.
Understanding the Role of Mitochondria
The energy produced by mitochondria, in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), is essential for the healthy functioning of organs throughout the body. ATP releases energy when broken down and fuels crucial bodily processes. While the brain, liver, heart, kidneys, muscles, gastrointestinal tract, and lungs consume the majority of this energy, mitochondria also play a key role in other bodily functions. They contribute to maintaining a healthy hormonal balance and are responsible for the adequate secretion of hormones. When mitochondria function declines, the brain experiences a decrease in sex steroids like estrogen and testosterone, which can lead to premature aging, particularly in women.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Exploring the Consequences
Mitochondrial dysfunction refers to the impaired ability of mitochondria to function properly. When mitochondria fail to generate sufficient energy levels, symptoms of insufficiency manifest in the body. These symptoms may include fatigue, mood swings, brain fatigue, anxiety, joint and lung diseases, indigestion, impaired speech, seizures, and strokes. Since these symptoms often overlap with those of other diseases, mitochondrial dysfunction can be challenging to diagnose. However, suspicion of mitochondrial dysfunction arises when three or more organs are affected. If you suspect dysfunction in multiple organs, seeking immediate medical attention for proper diagnosis is crucial. Moreover, mitochondrial dysfunction has also been linked to neurodegenerative diseases like cancer, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s, as well as endocrinologic diseases such as thyroid disorders and type-2 diabetes.
Identifying Factors Contributing to Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Multiple factors can contribute to poor mitochondrial function, with varying degrees of impact. A comprehensive diagnosis is essential to pinpoint the precise causes of mitochondrial dysfunction. Several physiological factors, such as environmental conditions, smoking, air pollution, exposure to certain chemicals, drugs, or genetic abnormalities, can affect mitochondrial function on a cellular level. Common cellular issues include improper functioning of the electron transport chain, reduced electrical and chemical transmembrane potential of the inner mitochondrial membrane, and impaired transport of critical metabolites into mitochondria. While it is often believed that mitochondrial diseases are solely inherited from the mother due to mitochondrial DNA inheritance, it is a misconception. Mitochondrial diseases can affect both organ systems and are inherited from maternal and paternal chromosomes.
Mitochondria and Aging: Unveiling the Connection
Aging is a natural process characterized by a decline in physiological and biological functions. Mitochondrial dysfunction plays a significant role in the aging process, particularly in women, as it contributes to decreased levels of sex steroids, such as estrogen. When mitochondria function poorly, there is a decline in the production of sex steroids in the brain, including estrogen and testosterone. These hormones are crucial for overall well-being and must be maintained at optimal levels to promote good health.
Promoting Hormonal Balance through Mitochondrial Care
Mitochondrial diseases can disrupt hormone production and balance in the body, leading to reduced energy levels, increased stress, and various internal problems. Cholesterol levels also significantly impact mitochondrial function. If cholesterol levels are high, it can contribute to mitochondrial dysfunction. It is advisable to follow a diet that helps maintain normal cholesterol levels or lowers high levels. A balanced diet plays a pivotal role in promoting proper hormonal functioning. The nutrients from your diet are broken down by mitochondria, which then provide energy to all major organs in the body. Therefore, if you are experiencing hormonal imbalances with fluctuating hormone levels, adopting a healthy balanced diet rich in proteins, carbohydrates, and essential nutrients is recommended. Additionally, considering the use of supplements to regulate hormone levels can be beneficial. However, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional before incorporating any supplements into your routine. Your doctor can diagnose any underlying issues and prescribe appropriate supplements, ensuring their safe and effective usage.
In Conclusion
Mitochondrial dysfunction can give rise to a wide range of diseases and disorders. As the primary energy producers and contributors to hormone production within the body, mitochondria play a crucial role in maintaining physical and mental well-being. If you observe any of the symptoms mentioned earlier or experience difficulties in more than three organs, it is essential to consult your doctor promptly. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage mitochondrial dysfunction and mitigate the associated effects on hormone production, thereby promoting overall health and vitality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Mitochondria not only provide energy for the body but also support the production of hormones such as estrogen, testosterone, progesterone, DHEA, and adrenal hormones. When mitochondria function poorly, hormone levels can decline, leading to imbalances and health issues.
Symptoms may include fatigue, mood swings, brain fog, anxiety, indigestion, joint pain, impaired speech, and even seizures or strokes. If three or more organs are affected, it may indicate mitochondrial dysfunction.
Contributing factors include environmental toxins, smoking, air pollution, chemical exposure, certain medications, genetic abnormalities, and issues with mitochondrial processes such as the electron transport chain and metabolite transport.
A healthy diet rich in proteins, carbohydrates, and essential nutrients helps mitochondria function properly, which in turn supports hormone balance. Managing cholesterol levels and consulting a doctor about supplements can also promote healthier hormone production.