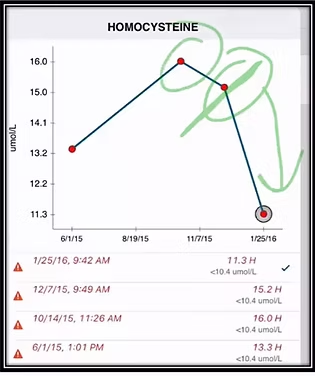
High levels of homocysteine, an amino acid derived from a common dietary amino acid, can pose significant risks to your health. This article aims to shed light on the dangers associated with elevated homocysteine levels and provide insights into the potential causes and prevention methods. By understanding the impact of high homocysteine and taking proactive measures, you can safeguard your well-being and reduce the risks of various health conditions.
Homocysteine has been linked to several health conditions, and maintaining optimal levels is crucial for overall well-being. Let’s explore some of the risks associated with elevated homocysteine levels:
Dementia:
Studies have shown a strong correlation between high homocysteine levels and an increased risk of dementia. Individuals with homocysteine levels exceeding 13.8 are more likely to develop silent brain infarcts and severe white matter lesions, contributing to cognitive decline.
Alzheimer’s:
High homocysteine levels can contribute to the degeneration of the brain, making individuals more susceptible to Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.
Pregnancy Complications:
Pregnant women with elevated homocysteine levels may experience complications such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and recurrent miscarriages. Monitoring and managing homocysteine levels during pregnancy is essential for maternal and fetal health.
Poor Concentration and Underachievement:
Excess homocysteine can impair cognitive function, leading to difficulties in concentration, memory, and overall academic or professional performance.
Cardiovascular Disease:
Elevated homocysteine levels have been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks, strokes, and atherosclerosis. Homocysteine can cause damage to the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, leading to inflammation and the formation of plaques.
Osteoporosis:
High homocysteine levels may contribute to the development of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures.
Diabetes:
Studies suggest a link between elevated homocysteine levels and an increased risk of developing diabetes. High homocysteine may impair insulin sensitivity and contribute to insulin resistance.
The Impact of Homocysteine on Your Blood Vessels:
The thin cell walls of your blood vessels are susceptible to damage caused by high homocysteine levels. This damage can lead to the leakage of blood components into different systems, triggering immune responses that may result in autoimmune conditions. Regular monitoring of homocysteine levels is essential to identify and address potential risks to your blood vessels and overall health.
Homocysteine and Brain Health:
As mentioned earlier, high homocysteine levels can contribute to the degeneration of the brain, potentially leading to conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Leakage of homocysteine into the brain can have catastrophic consequences, emphasizing the importance of maintaining optimal homocysteine levels for long-term cognitive health.
Possible Causes and Prevention:
Research indicates that deficiencies in certain vitamins and dietary compounds can contribute to increased homocysteine levels. By addressing these deficiencies through supplementation, you can potentially mitigate the risks associated with high homocysteine. Vitamin B12 and folate, both essential for the methylation cycle and gene reproduction, play a crucial role in regulating homocysteine levels.
To identify the main cause of elevated homocysteine, testing methylmalonic acid levels can help determine if the functional deficiency lies in vitamin B12 or folate. Once the deficiency is identified, appropriate supplementation can be initiated.
Preventing high homocysteine levels can be achieved through various measures:
Increase Vitamin B12 Intake: Incorporate dark, leafy greens such as kale, spinach, Swiss chard, and collard greens into your diet. Additionally, include food sources rich in vitamin B12 like sunflower seeds, fish, eggs, cheese, beans, walnuts, asparagus, and whole grains.
- Minimize Conventional Animal Proteins, Sugar, and Saturated Fats: Limiting the consumption of these foods can help preserve your body’s vitamin stores and regulate homocysteine levels.
- Avoid Processed and Canned Foods: These foods often lack essential vitamins, including B vitamins, due to processing methods. Opt for fresh, whole foods to ensure an adequate nutrient intake.
- Limit Caffeine Intake: Excessive caffeine consumption can deplete your B vitamin levels, potentially affecting the regulation of homocysteine. Moderation is key.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Limit alcohol intake to three drinks per week, as excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with the methylation cycle and elevate homocysteine levels.
- Adopt a Smoke-Free Lifestyle: Smoking has detrimental effects on overall health and can exacerbate the risks associated with high homocysteine levels.
- Be Aware of Medications: Certain medications, such as some antibiotics and contraceptives, can interfere with the methylation cycle. Consult your healthcare professional to discuss potential alternatives or supplementation strategies.
- Maintain Healthy Gut Bacteria: Probiotic supplements can support the proper absorption of vitamins, including B vitamins, from your food, aiding in homocysteine regulation.
- Improve Stomach Acid: Use herbal digestives (bitters) or consider supplemental hydrochloric acid (HCl) to enhance stomach acid production, which facilitates the absorption of vitamins.
- Incorporate Homocysteine-Reducing Supplements: Antioxidants, magnesium, and zinc have shown promise in reducing homocysteine levels. Consider including these supplements in your routine after consulting with your healthcare professional.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult your doctor to discuss suitable supplements that can support healthy homocysteine metabolism, such as folate supplements.
Conclusion:
Maintaining optimal homocysteine levels is crucial for overall health and reducing the risks associated with various conditions, including dementia, cardiovascular disease, and osteoporosis. By understanding the dangers of high homocysteine, identifying possible causes, and taking preventive measures, you can protect your well-being and promote a healthier future. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance on managing homocysteine levels effectively.
Video time stamps
[00:00:03] homocysteine
[00:00:45] high homocysteine
[00:01:00] can actually damage the interior endothelial
[00:01:25] dementia, it can cause pregnancy complications, poo concentration, cardiovascular disease,
[00:01:35] osteoporosis and diabetes
[00:02:35] immune system
[00:02:45] leaky gut
[00:03:35] functional range
[00:03:45] major inflammation,
[00:03:50] brain fog, autoimmune conditions
[00:03:55] Homocysteine is not a very pleasant marker to have elevated
[00:04:40] So this is an amazing drop when it comes to homocysteine
[00:05:50] His vitamin D was in the tank
[00:06:00] functional medicine
[00:06:05] itchy and break down digestive problems
[00:06:40] . Brain infarction
[00:06:45] where your brain is dying
[00:07:05] is dying, is 2.5 times greater than someone that would have a normal homocysteine
[00:08:00] leaks out in the brain and causes death to your brain and all your tissues
[00:08:15] your brain here as these white matter lesions
[00:09:30] the brain is actually starting to degenerate and homocysteine
[00:09:35] homocysteine levels elevated homocysteine levels
[00:10:30] brain lesions, brain fog, Alzheimer’s disease
[00:10:55] chronic inflammation, you can just assume that if you have high homocysteine
[00:12:00] blood vessels
[00:12:10] is causing an autoimmune reaction
[00:13:35] that progression of vascular dementia
[00:13:40] Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s disease
[00:13:45] anemia
[00:14:15] homocysteine is a really critical marker for DNA production.
[00:14:25] DNA
[00:17:05] sluggish genes
[00:17:45] recycling and it’s getting rid of homocysteine right here
[00:18:00] methyl group on the DNA
[00:18:15] Floxed medicine
[00:18:25] high homocysteine, I guarantee you that this little methyl group
[00:19:45] methyl group on the DNA
[00:21:30] any methyl groups
[00:21:50] was prone to diabetes and cancer
[00:23:30] decreases your just your risk of cancer and and diabetes
[00:24:40] homocysteine builds up
[00:26:27] functional medicine
[00:27:45] magnesium and zinc
[00:27:55] B12, B6
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Elevated homocysteine is associated with dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular problems, pregnancy complications, poor concentration, osteoporosis, and diabetes.
While the conventional lab range is 0–10.4 µmol/L, the functional medicine range of 5–8 µmol/L is considered ideal for protecting long-term health.
High levels can damage blood vessels in the brain, increasing the risk of white matter lesions, cognitive decline, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia.
Eat foods rich in B vitamins (leafy greens, fish, eggs, nuts, whole grains), limit processed foods and alcohol, avoid smoking, support digestion, and consider supplements such as folate, B12, magnesium, and zinc under professional guidance.
Autoimmune diseases involve a dysregulated immune system that attacks the body's own tissues. This constant state of activation and confusion can lead to exhaustion and depletion of white blood cells over time. Therefore, a chronically low WBC count is not just a symptom but a key indicator of an overworked and compromised immune system often seen in autoimmune conditions.